Abu Dhabi: The UAE National Food Security Strategy aims to develop sustainable local production enabled by technology for the entire value chain, and to establish smart technologies in food production.
The objective is to top the global food security index by 2051.
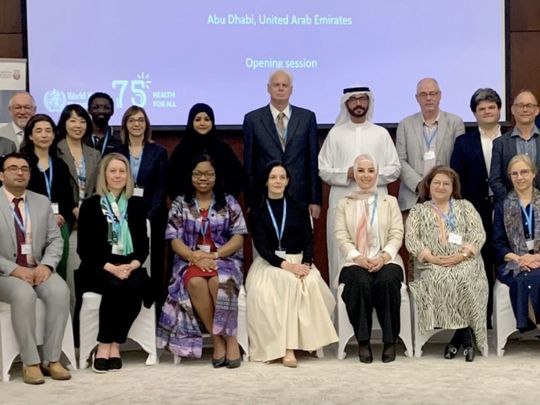
As part of this strategy, the Abu Dhabi Agriculture and Food Safety Authority (ADAFSA) hosted the World Health Organisation’s Foodborne Disease Burden Epidemiology Reference Group (FERG) conference in Abu Dhabi on April 1.
FERG members and WHO representatives discussed methodologies for estimating the burden of foodborne disease, indicators for monitoring global progress and action plans.
In her opening speech, Mouza Suhail Al Muhairi, Deputy Director-General for Regulatory and Administrative Affairs at ADAFSA, said: “Abu Dhabi is a vibrant city where food safety is the cornerstone of ensuring the wellbeing of the community. ADAFSA is committed to improving food safety at the local level, and we believe that international cooperation is necessary to address challenges related to food safety and security.”
WHO representative Dr Elaine Borghi highlighted the importance of bringing together experts from around the world to share knowledge and experience on the burden of foodborne diseases and to formulate effective strategies to reduce their impact on public health.
“Foodborne diseases cost the global economy around $110 billion annually. Sustainability and building sustainable food systems cannot be achieved without addressing food safety concerns within the food chain,” she said.
In 2022, WHO member states adopted the Global Strategy for Food Safety 2022-30 for stronger food safety systems and global collaboration.
The conference delved into reviewing and analysing data collection methods, ultimately determining a methodology for estimating the burden of foodborne diseases at national, regional and global levels. Participants also developed indicators to monitor progress in reducing the burden, exchanged best practices, and formulated recommendations to strengthen food safety globally.