Abuja (Nigeria): The calls for him to quit were already loud, coming from two former presidents, a prominent pastor and newspaper editorials. Even Catholic bishops weighed in with criticism.
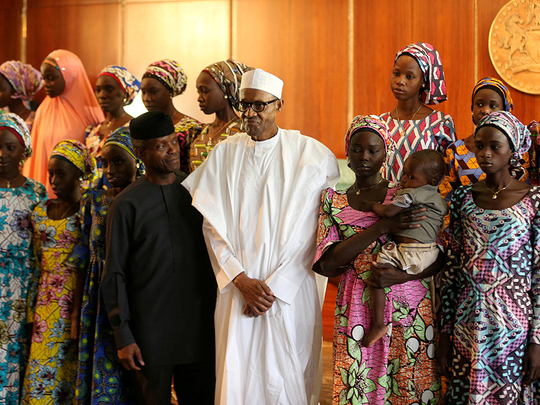
Now, the president of Nigeria is facing a new crisis: the mass kidnapping of 110 girls from their school late last month, prompting another wave of outrage at the government.
The pressure is mounting on President Muhammadu Buhari to step down after his first term expires next year. A diverse range of Nigerians have joined the chorus, and while the presidential vote is still almost a year away, campaign season in Nigeria is in full swing. Billboards have popped up in parts of the country and election news dominates the headlines.
Nigeria’s constitution allows Buhari to seek a second term, but his opponents and former allies are piling on. Even his wife has emerged as a detractor of sorts, using social media to post video clips of politicians criticising her husband’s presidency.
The latest tragedy gripping the nation — the 110 girls who went missing in the town of Dapchi after militants attacked their school — has only deepened the scepticism of Buhari. He has been criticised for being slow to speak out about the attack, especially after he swore that something like this would never happen again after a similar kidnapping in 2014 of nearly 300 schoolgirls from Chibok.
Then on Friday, Buhari came under more criticism after militants began a major attack on a military installation near a displaced persons camp in the town of Rann, killing at least three aid workers and several others. Three people were missing amid fears they had been kidnapped. The same camp was erroneously struck by Nigeria’s own military jets last year, killing dozens of displaced people and aid workers.
Buhari has not announced whether he will seek a second term. His aides have indicated that he will, arguing that other aspirants have nothing to offer Nigeria, the continent’s most populous nation.
“Buhari has already transformed and changed the image of leadership and that of our leaders in this country, both locally and internationally,” said Boss Mustapha, secretary to the federal government.
Buhari, a retired general, transfixed voters in 2015 with his promises to lift the nation’s troubled economy, end decades of corruption and win the war with Boko Haram, the Islamist militant group that has claimed thousands of lives and uprooted millions from their homes in the north of the country.
All those problems are still festering.
“This goodwill is being fast depleted by some glaring failures of government,” said Archbishop Ignatius Ayau Kaigama, until recently president of the Catholic Bishops Conference of Nigeria, which said living conditions have worsened under Buhari.
Critics also cite Buhari’s health as a concern. He spent weeks at a time last year in London receiving treatment for an illness whose nature he has yet to disclose.
In his time in office, a secessionist movement championed by a group called the Indigenous People of Biafra has gained steam in the southeast of the country, 50 years after a civil war over the same issue left one million people dead. Under Buhari, military operations have led to dozens of arrests and deaths, and the disappearance of the movement’s leader.
Beyond that, conflicts between farmers and pastoralists looking for places for their cattle to graze have escalated, with recent bouts of violence killing dozens.
Critics complain that Buhari has failed to resolve these tensions. But even his opponents concede that he has tried to work on the promises that helped him win the presidency.
Almost as soon as he began his term, Buhari began an assault against Boko Haram, with the military taking back territory and capturing and killing scores of militants. His government negotiated the release of several dozen of the students taken in 2014 from Chibok. Two other groups of high-profile hostages — female police officers and university professors — were released this year.
But those successes have been marred by the new kidnappings at the Dapchi school. Officials didn’t initially label the episode a kidnapping, despite numerous witnesses reports of militants hauling away the girls. The president’s aides would say only that the girls are missing.
The war with Boko Haram still rages, with suicide bombers pulling off regular attacks and militants conducting increasingly complex operations. About 100 students from Chibok are still held hostage.
Yet Buhari has baffled the nation by repeatedly saying Boko Haram has been defeated.
His government has worked to crack down on corruption, uncovering millions of dollars’ worth of cash and making high-profile arrests.
But critics say corruption is still widespread. They were outraged that Buhari hired a former director of the nation’s pension fund to a new post in his government after the previous administration had fired the man on grounds he had pilfered billions.
In Nigeria, informal agreements call for the presidency to alternate every two terms between someone from the predominantly Muslim north — where Buhari is from — and a person from the Christian south. If Buhari does not seek a second term, many Nigerians will expect the presidency to go to a fellow northerner.
Buhari maintains a significant base in northern states, but he will need to build more support in other regions to win another term. Analysts are buzzing about suitable replacements.
Potential contenders include Atiku Abubakar, who served as vice-president from 1999-2007. He is a co-owner of one of Nigeria’s largest oil and gas logistics companies and the founder of the American University of Nigeria, a private institution. Another possible candidate is Sule Lamido, a former foreign minister. Both men are members of the opposition People’s Democratic Party.
Bola Tinubu, national leader of Buhari’s party, the All People’s Congress, was recently appointed by Buhari to lead reconciliation and confidence-building efforts among party members. Many analysts believed the move was intended to assuage feelings that Tinubu had been sidelined during Buhari’s administration. Some speculate Tinubu could make a bid for the presidency himself.
Tunde Bakare, a well-known pastor who was once Buhari’s running mate, has also become a vocal opponent.
“This administration anchored its policy outlook on three main thrusts, including security, job creation through diversification, and anti-corruption,” Bakare said in what he called his own state of the nation speech. “Yet all around us are signs of retrogression.”