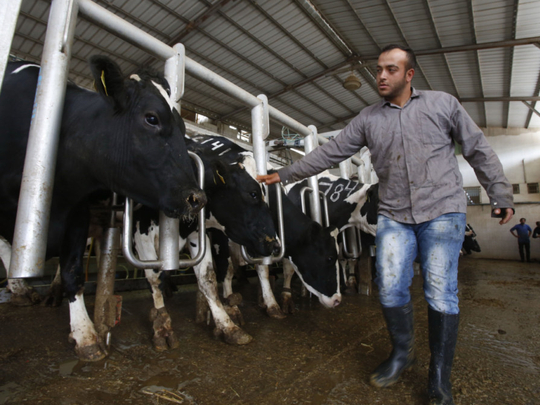
Dahriyah, West Bank: Power comes in many forms, but Kamal Al Jebrini’s family looked to where others may fear to tread for a new source of it: cow dung.
The family has begun recycling waste from its cows to produce electricity for one of the largest Palestinian dairy plants and even to provide power to some houses.
They discovered the idea during trips abroad and decided that cow dung that would otherwise mainly rot in the sun — apart from some used as fertiliser by neighbouring farmers — could be put to better use.
“It was a shame to allow all of that manure to be lost and impact the environment when we can produce electricity with it,” said Al Jebrini, who owns a large farm of about 1,000 cows with his brothers.
He spoke after inspecting the milking room, where workers look after lumbering cows.
The project in the occupied West Bank is the first of its kind in the Palestinian territories, where renewable energy usually means solar panels.
The family turned to Maher Magalsay, who specialises in renewable energy at the Polytechnic University of Hebron, the major city located nearby in the south of the West Bank, which has been occupied by Israel for 50 years.
Magalsay brought engineers and a large generator from Germany to develop the project that involves using heat to produce methane and biogas from the cow dung to run turbines. He involved his students, including some former students who had done apprenticeships abroad.
Magalsay proudly shows off two large silos where manure and biogas are stocked for later use. It allows the 30 tonnes of dung produced daily by Al Jebrini’s cows to generate 380 kilowatt hours of power. That’s enough to no longer have to pay electricity bills for his company, which sells milk, yoghurt and other dairy products throughout the occupied West Bank and occupied Jerusalem, said Al Jebrini. He can even route part of the energy produced to the local electricity company.
There is no power plant in the West Bank, and nearly 90 per cent of the 5.3 gigawatts of power consumed there comes in via the Israeli grid.
For certain regions, the bills are taken care of by local authorities or the Palestinian National Authority.
When unpaid bills have stacked up, Israel has often cut power to Palestinian territories.
Israeli authorities have long called for the payment of debt for electricity provided to the occupied West Bank and occupied east Jerusalem that they estimate to be some $475 million (Dh1.74 billion). At the same time, around four per cent of Palestinian villages are not connected to the electricity grid, according to official data.
Most of the villages that are off the grid are in the Hebron area — making Al Jebrini’s project even more relevant and an example to be emulated.
It certainly doesn’t seem to trouble the cows and calves who munch straw under sheet metal roofs.
Their owners hope to do even more.
“In the next phase, we are going to use another generator to produce 650 kilowatt hours and, over the long term, we will reach one megawatt hour,” said Magalsay.
With that amount, “we could supply between 200 and 300 houses,” he said.